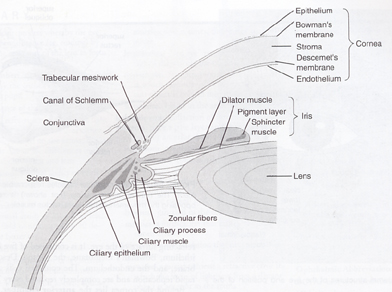
The Ciliary Body
Definition
A part of the eye
anterior continuation of the choroid
Structure and function
Consists of non-striated muscle fibres (ciliary muscle) and secretory epithelial cells.
The suspensory ligament which holds the capsule of the lens is attached to the ciliary body.
The contraction of the ciliary muscle changes the thickness of the lens so that it can focus the light on the retina. (accommodation)
The epithelial cells secrete aqueous fluid into the anterior segment of the eye
When the ciliary muscles contract the thickness of the len increases and the near objects are focused on the retina better
Nerve supply
Parasympathetic branches of the oculomotor nerve (3rd cranial nerve)
Applied Anatomy
Old age - weakness of the ciliary body (ciliary muscle) - inability to thicken the lens to observe nearby object - Presbyopia.